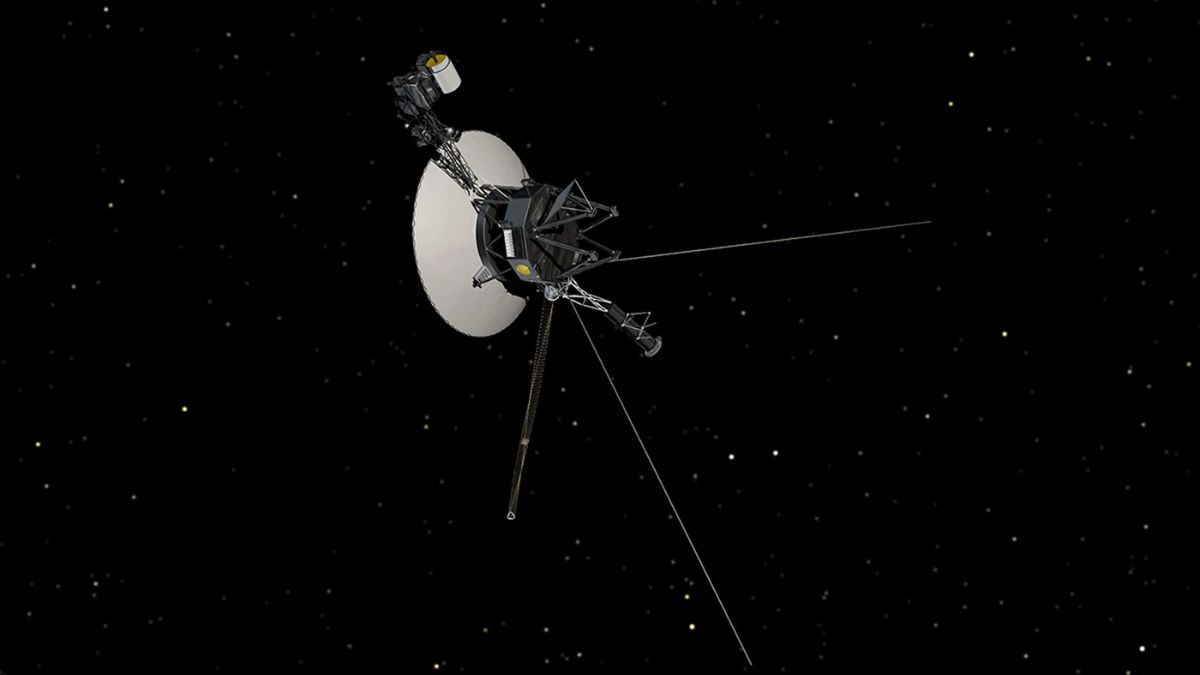
Voyager 1, humanity’s farthest and most enduring spacecraft, is about to hit a cosmic milestone that might just blow your mind: by November 15, 2026, it will be so far from Earth that a radio signal will take exactly 24 hours—one full light-day—to reach it. Think about that for a moment. Send a message today, and it won’t even arrive until tomorrow. Then, it’ll take another 24 hours to hear back.
It’s the latest surreal moment in the long, lonely journey of this legendary deep-space probe—and a humbling reminder of just how massive the universe really is.
Table of Contents
Distance
As of now, Voyager 1 is roughly 15.7 billion miles (25.3 billion kilometers) from Earth. That’s about 23 hours and 32 minutes of one-way light travel. Every second, it gets a little bit farther—closing in on that magical 16.1 billion mile mark, when it will officially be one light-day away.
Let’s put that into perspective with some comparisons:
| Location | Distance from Earth | One-way Light Time |
|---|---|---|
| Moon | 226,000 miles | ~1.3 seconds |
| Mars (avg.) | 140 million miles | ~4 minutes |
| Jupiter | 484 million miles | ~52 minutes |
| Pluto | 3.7 billion miles | ~6.8 hours |
| Voyager 1 (2026) | 16.1 billion miles | 24 hours |
That’s not just far. That’s “phone call turns into a two-day conversation” far.
Delay
We usually don’t think of light having a travel time. Flip a switch, and the room lights up instantly. But in space, the speed of light becomes a noticeable bottleneck. This was first seen during the Apollo moon landings, where communication between astronauts and Houston was always a few seconds behind.
The further you go, the more that delay grows—and by the time you’re dealing with Voyager 1, it’s not just inconvenient. It’s a full-on logistical challenge.
If engineers want to send a command to Voyager 1 in 2026:
- It’ll take 24 hours to reach the probe.
- It’ll take another 24 hours for Voyager to respond.
- That’s two full days just to confirm a single command.
It’s no wonder Voyager had to be built to think for itself—there’s no time for back-and-forth when you’re flying blind.
Journey
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 was originally just meant to visit Jupiter and Saturn. But after completing its mission, it kept going—and going. Now, it’s cruising through interstellar space, beyond the bubble of the Sun’s influence.
Its nuclear power source is running low, and scientists expect it will go silent within the next year or two. Still, it’s remarkable that a spacecraft built in the 1970s is still operating almost 50 years later, in one of the most extreme environments known to man.
Status
Even though it’s running on ancient hardware, Voyager 1 is still talking to NASA, thanks to the Deep Space Network—a system of massive radio antennas around the world.
Here’s where both Voyagers stand right now:
| Spacecraft | Distance (approx.) | Light Travel Time |
|---|---|---|
| Voyager 1 | 15.7 billion miles | ~23 hours, 32 minutes |
| Voyager 2 | 13.1 billion miles | ~19.5 light hours |
Both probes still return valuable data, especially on cosmic rays and interstellar particles, as they’re the first human-made objects to ever reach this far.
Legacy
Even when Voyager 1 eventually falls silent, it won’t be forgotten.
- It carries the Golden Record, a message from Earth filled with music, sounds, and greetings from humanity.
- It’s expected to continue drifting through space for billions of years, possibly outliving our civilization.
- It’s a symbol of human curiosity—proof that we were here, and that we reached for the stars.
When you hear that it’s a light-day away, think of what that really means: we’ve sent a piece of ourselves so far that it takes a full Earth day for light to catch up. That’s not just a scientific milestone—it’s a profound, poetic one.
So, the next time your Wi-Fi lags or your texts take a second to send, just remember: out there, Voyager 1 is waiting… 24 hours for your signal to arrive.
FAQs
How far is Voyager 1 from Earth now?
About 15.7 billion miles or 23.5 light hours away.
When will Voyager 1 be one light-day away?
Around November 15, 2026, based on current speed.
What is a light-day?
The distance light travels in 24 hours—about 16.1 billion miles.
Is Voyager 1 still working?
Yes, but its power source may fail in the next 1–2 years.
Can we still talk to Voyager 1?
Yes, through NASA’s Deep Space Network—though with long delays.